Codigo Escuela 4.0
Article author:
Sergio PeciñaArticle published at:
March 16, 2025
Drawer menu
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) filament is the most popular flexible material for 3D printing because of its great versatility. It's high durability and flexibility make it ideal for prototyping and even final products.
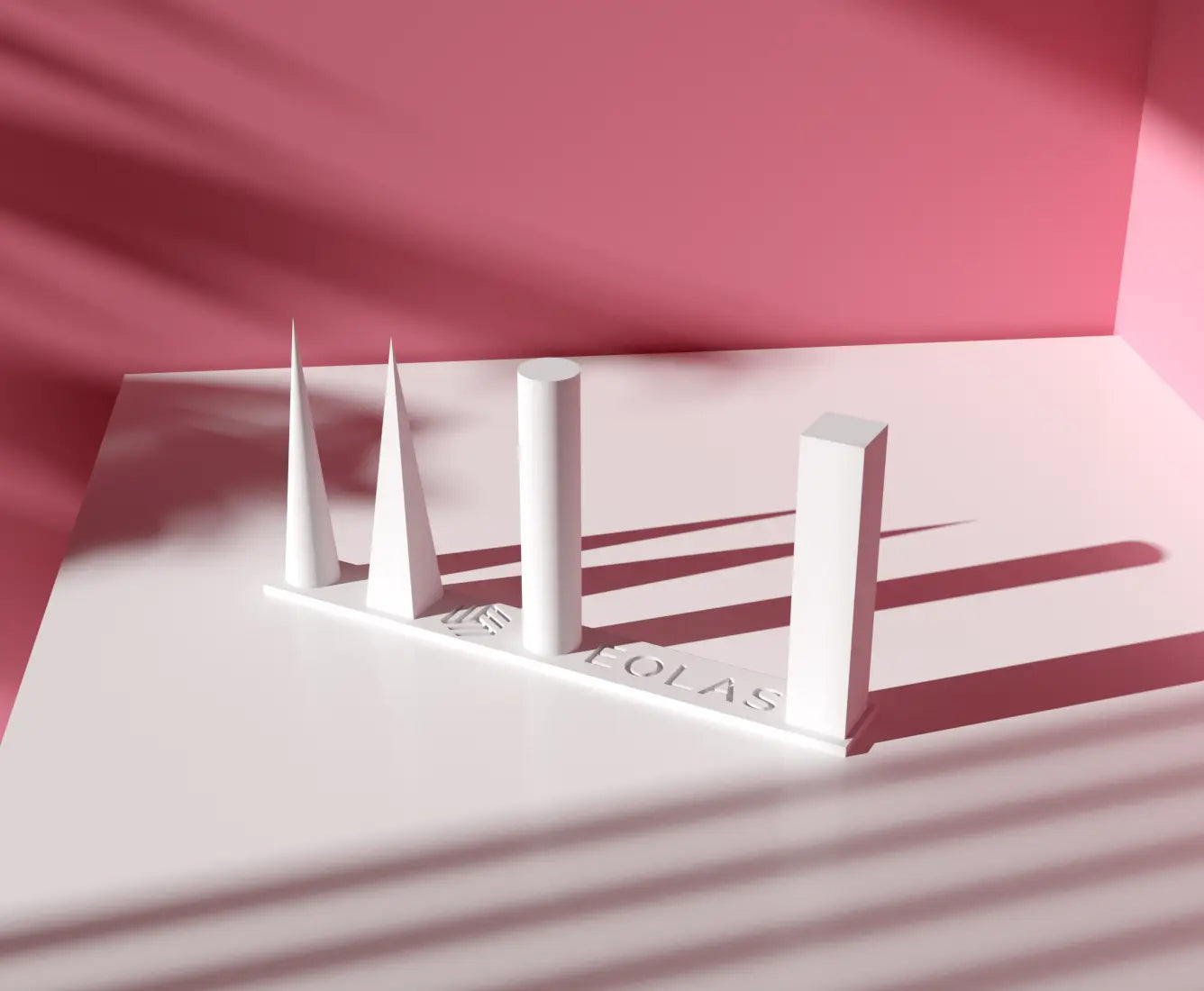
The correct temperature for extruding this material depends largely on your extrusion system. The range is 195°C to 240°C. The lower the temperature required to extrude the material, the better, as it will expand less (have less diameter increase). You will determine the correct parameter values for your 3D printer by performing a temperature test on this material.
The material has excellent adhesion, so it does not require a hot bed to stay attached to the base material. Even so, if you desire, you can operate at temperatures as low as 50°C. If you're printing on a smooth PEI surface, you must apply an adhesive (glue stick or lacquer) to create a barrier between the PEI and the component, or else it will be extremely difficult to remove the component from the surface.
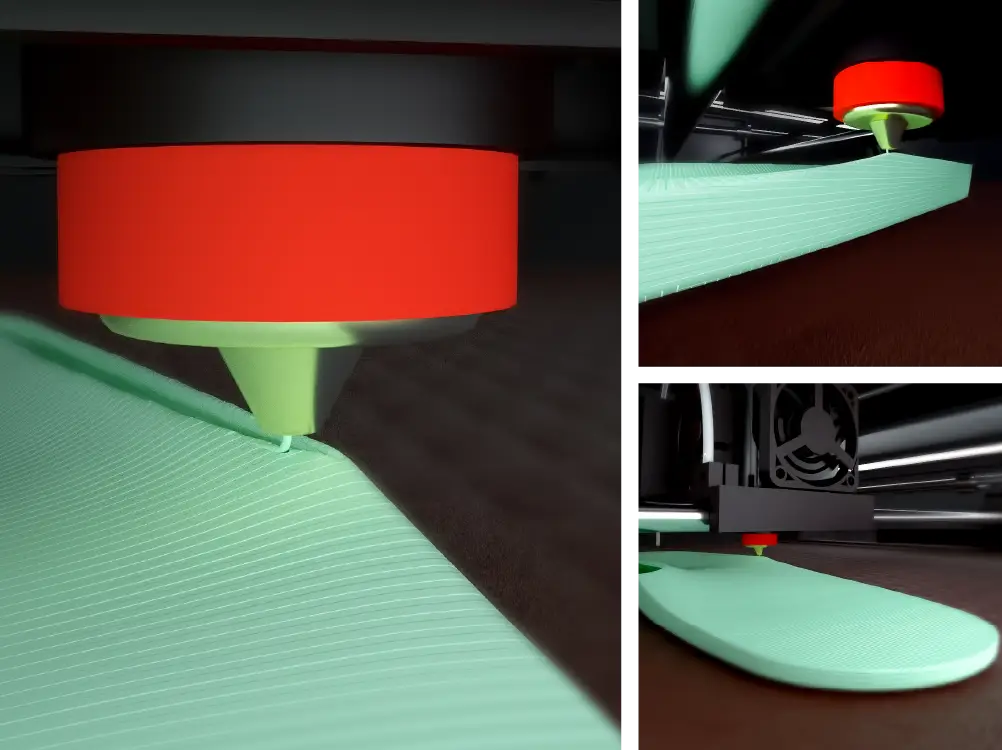
When a part has a lot of detail, it is critical to help the plastic properly solidify so that it adheres properly. It is not advised to turn on this fan in the initial layers to enhance the part's adhesion to the surface.
Because it is such a flexible material, the printing speed will be slow so that the material can flow smoothly through the hotend. Average speeds of around 15-20mm/s for normal prints and 5-10mm/s for more precise prints are recommended, but these values are just guidelines. We advise keeping the speed below 35mm/s to ensure proper material extrusion. Each machine has a speed limit, which is best determined through experimentation and then reduced slightly to ensure proper printing with TPU and to prevent jams.
The optimum layer height is usually 50% of the nozzle outlet diameter, but it can be lowered to 25% or raised to 75-80%. For a 0.4mm nozzle, an optimum layer height would be 0.2mm within a range of 0.1mm and 0.3mm.
It is critical to monitor the filament's tolerance to ensure it doesn't excessively stretch or compress as it moves through the printer. To be sure of the proper values, a test must be performed for every material used in the printer. With this material, it is common for the values to be over 100% to counterbalance the deformation caused by the extruder's thrust zone. The steps per millimetre must be precisely calibrated on the extruder to obtain this parameter correctly.

The retraction value should be determined by testing using the hotend and extruder setup, to guarantee the best results. At first, you should print without retraction if you're using a flexible material since it doesn't handle shrinkage very well. However, you can use this variable when printing with TPU to improve your results if you have calibrated the other variables; the following estimates may be of help: