Codigo Escuela 4.0
Article author:
Sergio PeciñaArticle published at:
March 16, 2025
Drawer menu
ABS is the most widely used plastic in the world, it has great mechanical and thermal properties. It was the first plastic to be commercialised in 3D printing.
The temperature range for this material is between 235°C and 250°C, the correct temperature depends mainly on the size of the nozzle and the extrusion system of the machine. With ABS, the hotter the material is extruded, the better the flow and the stronger the adhesion between layers. To know the correct temperature it is necessary to do a temperature test, but a starting temperature can be 240°C.
For the correct adhesion of this material it is necessary to use a hot bed between 90ºC and 110ºC. The use of any specific adhesive for high temperature 3D printing will be very useful to avoid the dreaded "warping" effect; we recommend the use of these adhesives for large parts. It is also possible to print on a smooth or textured PEI surface, greatly improving the adhesion of the first layer. Do not hesitate to use the raft or brim function with this material as it will help to prevent warping in the printing process.
This material benefits when printed at low speed, as the high temperature and the slightly slower speed improve the adhesion between layers. Also if the speed is slower, the material is allowed to cool down before the top layer is deposited.
About 20mm/s for the first layers will ensure proper adhesion to the printing surface, avoiding warping as much as possible. Gradually increase the speed as the part grows (if your slicer allows) until we have a speed that allows the deposited material to cool down before adding another layer on top. A speed of 55 - 60mm/s is a speed with a good balance between quality and time.
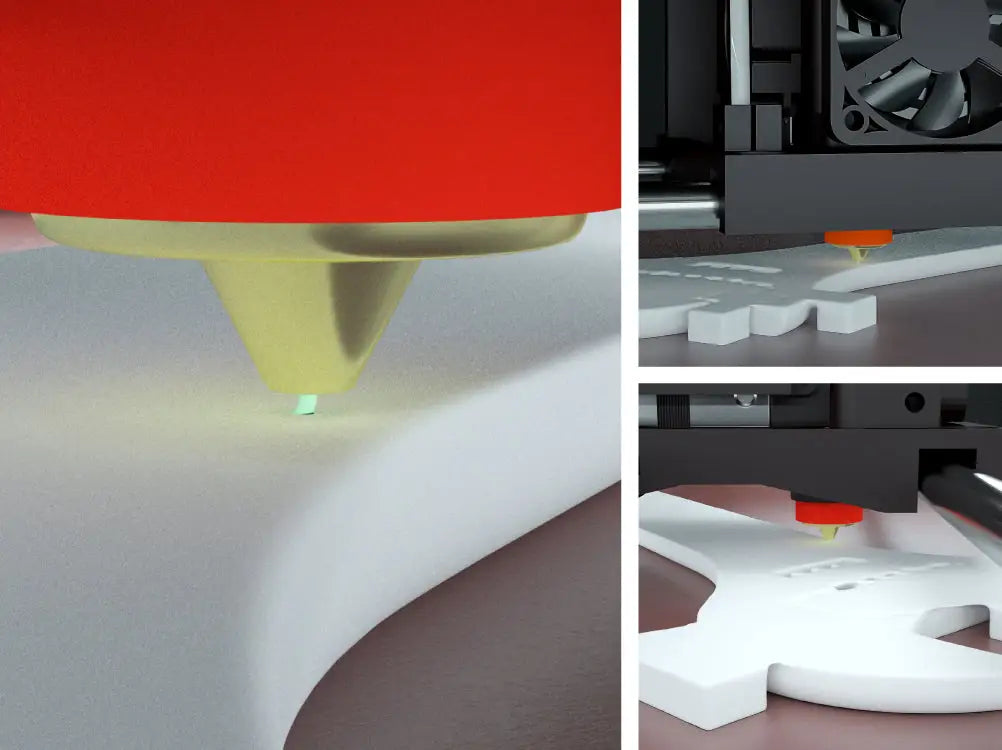
The use of this fan is not recommended, as it promotes the cracking effect by rapidly cooling the deposited material.
The layer height is determined by the outlet diameter of the nozzle, the optimum value is usually 50% of this diameter although it is possible to go up to 75-80% and down to 25%. For a 0.4mm nozzle, the optimum coating height would be 0.2mm and the maximum values would be 0.3mm and 0.1mm.
This parameter is in charge of absorbing the dimensional tolerance of the filaments, so it is necessary to carry out a test to know the exact value for each material. This parameter in a normal print should not vary more than 5%, that is to say that this parameter has to be between 95% and 105%. If after performing the flow test our parameter is out of this range, our extruder is badly calibrated and we must calibrate it first to obtain the optimum results.

This parameter depends on the hotend - extruder assembly and it is necessary to perform a retraction test to obtain an optimum value. Initial retraction values can be as follows: